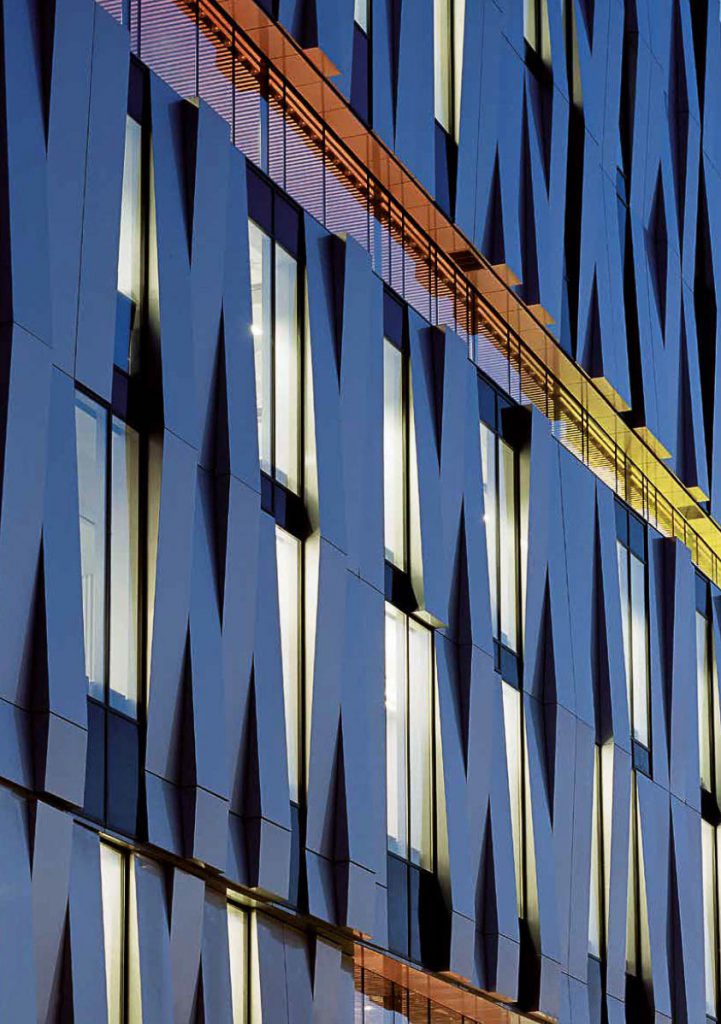
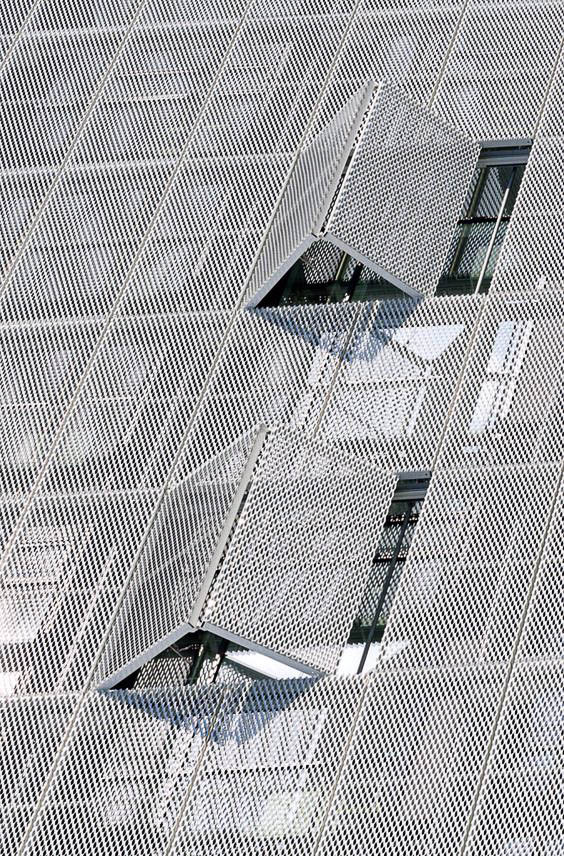
Humans create spaces to utilize them; they then create walls and claddings to cover and protect those spaces from harm and undesirable conditions further creating a sense of privacy. As humans and their modernistic societies become more complex, so does the evolution and role of architecture. Thus, the idea of designing walls and cladding merely to cover ‘spaces’ has seemingly become obsolete as these elements are increasingly needed to serve more complex uses. Systems such as these are now also needed to reflect the identity of the particular architectural spaces they cover, much like cloths that not only cover the wearer, but reflect their identity beneath. The context of modern society and ever-evolving technology allows architects to freely choose materials and develop new techniques and technologies for these systems that both serve the purposes of a particular architecture as well as hinting or display its identity, resulting in skins of modern works that are more dimensionally suggestive and visually interesting when compared to their older counterparts. This article will discuss various materials for wall cladding, from older systems using wood, stone and brick to precast concrete and modern materials including glass and curtain wall systems which are developed to serve various needs in terms of sturdiness, durability, safety, and environmental protection.
Text: Patikorn Na Songkhla
Photo Courtesy of Archiproducts, Dow, Media-TIC / Enric Ruiz Geli, Dezeen, Detail-Online, Galleria Centercity / UNStudio, Architectsjournal, Professionals.lysaght, and Alucobond except as noted
Download the online journal Issue 02 More Than Skin Click here
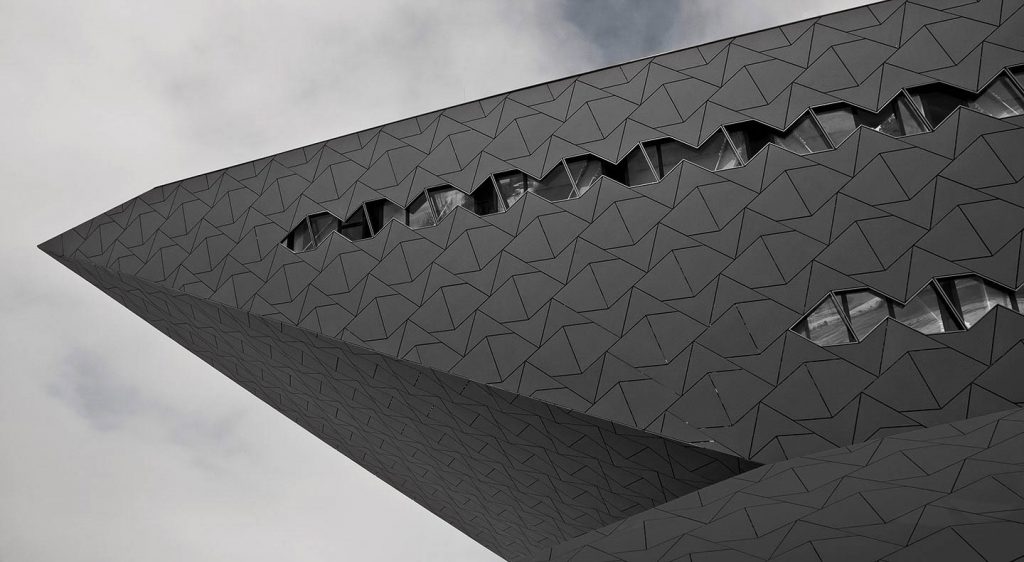

Photo: Equitone
มนุษย์สร้างที่ว่างหรือสเปซขึ้นเพื่อใช้งาน สร้างผนังและผิวผนังเพื่อห่อหุ้มสเปซ ปกป้องสเปซนั้นจากดินฟ้าอากาศและจากสิ่งที่ไม่พึงปรารถนา และสร้างความเป็นส่วนตัว เมื่อมนุษย์มีความซับซ้อนขึ้น สังคมซับซ้อนขึ้น ความเป็นอยู่และบทบาทของสถาปัตยกรรมก็ซับซ้อนขึ้นตามไปด้วย การออกแบบผนังและผิวผนังอาคารเพียงเพื่อห่อหุ้มที่ว่างกลายเป็นแนวคิดที่ตกเลือนไปจากยุคสมัย เพราะในสังคมสมัยใหม่ นอกจากผิวผนังอาคารจะต้องตอบสนองการใช้งานที่ซับซ้อนขึ้นแล้ว มันยังได้มีส่วนทำหน้าที่แสดงออกหรือสื่อสารตัวตนของสถาปัตยกรรม ไม่ต่างจากเครื่องนุ่งห่มที่ครั้งหนึ่งเป็นเพียงปัจจัยสำหรับปกคลุมร่างกายได้กลายมาเป็นสิ่งที่แสดงออกถึงตัวตนของผู้สวมใส่ในบริบทของสังคมร่วมสมัยและเทคโนโลยีที่พัฒนาไปไม่หยุดยั้ง ทำให้ผิวผนังอาคารมีมิติต่างๆ มากมายที่น่าสนใจ เมื่อสถาปนิกสามารถเลือกใช้วัสดุและพัฒนาเทคนิคในการสร้างผิวผนัง ในการตอบสนองการใช้งานและการแสดงออกได้อย่างเสรี แทนที่ผิวผนังอาคารในมิติเดิมๆ แบบในอดีต
จากผนังไม้สมัยโบราณ ผนังก่ออิฐมาเป็นผนังคอนกรีตสำเร็จรูป จากผนังฉาบปูนเรียบทาสีมาเป็นผนังใช้วัสดุห่อหุ้มสำเร็จรูปต่างๆ รวมถึงกระจกและระบบ Curtain Wall ที่มีการพัฒนาให้ตอบสนองประโยชน์ ใช้สอยทั้งในเรื่องความคงทน แข็งแรงปลอดภัย การป้องกันสภาวะอากาศที่เปลี่ยนแปลง การป้องกันการรั่วซึมของน้ำและอากาศ ส่วนหนึ่งของทางเลือกวัสดุผิวผนังภายนอกอาคารจะนำมาพูดคุยกันในวันนี้
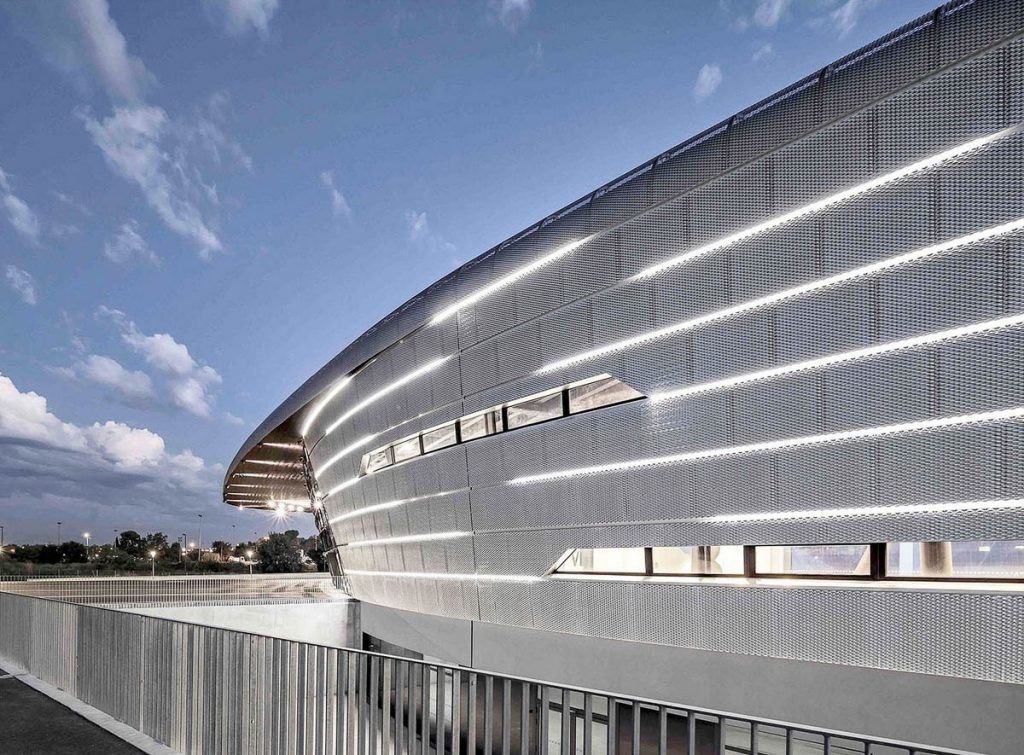

Photo: Archiproducts
External Cladding
Ludwig Hatschek คิดค้นไฟเบอร์ซีเมนต์ในปลายศตวรรษที่ 19 แผ่นวัสดุประเภทไฟเบอร์ซีเมนต์บอร์ดที่ประกอบด้วยซีเมนต์ เซลลูโลส และแร่ที่มาเติมแต่ง ได้มีการใช้งานอย่างแพร่หลายในช่วงเวลาต่อมา ไฟเบอร์ซีเมนต์บอร์ดเป็นวัสดุอาคารที่มีเอกลักษณ์เฉพาะตัวแสดงเนื้อสัมผัสดิบๆ ด้านในที่เป็นธรรมชาติ ถูกผลิตและนำเสนอเพื่อใช้การใช้ในรูปแบบต่างๆ ผลิตภัณฑ์ที่มีคุณภาพเหมาะสมเพื่อใช้งานเป็นผนังภายนอกอาคารได้ถูกพัฒนาขึ้น แผ่นวัสดุสามารถเจาะรูด้วย Waterjet หรือเครื่อง CNC สามารถทำให้เกิดลวดลายนูนสูงต่ำ ตัดจัดเรียงได้หลายรูปแบบ การออกแบบรายละเอียดโดยเฉพาะสำหรับงานผนังภายนอกอาคารเป็นเรื่องสำคัญ การออกแบบรอยต่อแผ่น ระบบการติดตั้ง โครงรองรับ และผนังด้านหลังมีผลต่อประสิทธิภาพการระบายอากาศ การป้องกันการรั่วซึมของน้ำ รวมถึงเรื่องการจัดการด้านพลังงาน
วัสดุประเภทแผ่นอะลูมิเนียมห่อหุ้มอาคาร หรือ Aluminium Cladding ใช้งานกันแพร่หลายในงานสถาปัตยกรรม ด้วยความสวยงามทันสมัย น้ำหนักเบามีความยืดหยุ่นและสะดวกในการติดตั้ง วัสดุเคลือบผิวช่วยให้มีความคงทนอายุการใช้งานยาวนาน มีทั้งประเภท Solid และ Composite แผ่นอะลูมิเนียมแบบ Solid มีความปลอดภัย ยั่งยืนเป็นมิตรกับสิ่งแวดล้อมผิวสำเร็จมีให้เลือกทั้งเป็นการเคลือบสีคุณภาพสูงประเภท Fluorocarbon หรือทำผิว Anodise แผ่นอะลูมิเนียมแบบ Composite ประกอบด้วยแผ่นอะลูมิเนียม บางสองแผ่นประกบไส้กลางพลาสติก แผ่นนอกมีระบบเคลือบสีประเภท Fluorocarbon ที่มีความคงทนต่อสภาวะอากาศ ไส้กลาง FR (Fire Resistant) รวมถึงไส้กลางอะลูมิเนียมแบบ Honeycomb ถูกนำมาตอบโจทย์เรื่องความปลอดภัยกรณีเกิดเพลิงไหม้และความแข็งแรง
ระบบการติดตั้งแบบ Mechanical ยังเป็นมาตรฐานการติดตั้งที่ใช้กัน ขณะที่การใช้เทปหรือกาวคุณภาพสูงได้รับการพัฒนาเป็นสิ่งประดิษฐ์เพื่อให้เป็นอีกทางเลือก การออกแบบรอยต่อ การเลือกใช้วัสดุยาแนวที่เหมาะสม การบำรุงรักษา ซ่อมแซม ทำความสะอาดคราบสกปรกที่จะเกิดขึ้น ล้วนเป็นสิ่งที่สถาปนิกต้องพิจารณาให้ความสำคัญ วัสดุแผ่นโลหะห่อหุ้มอาคาร หรือ Metal Cladding มีความคงทนแข็งแรง ขณะที่ให้ความยืดหยุ่น โลหะแต่ละประเภทมีคุณสมบัติที่แตกต่างกันไป ความสวยงามและราคาก็แตกต่างกันด้วย พื้นผิวอาจมีการทำระบบสีเคลือบหรือแสดงออกซึ่งธรรมชาติของวัสดุนั้น โลหะบางประเภทยังมีการเปลี่ยนแปลงทางกายภาพเมื่อเวลาผ่านไปทำให้ภาพลักษณ์ปรากเปลี่ยนไปเสมือนมีชีวิต เป็นหลากหลายทางเลือกวัสดุผนังอาคารให้กับงานสถาปัตยกรรม นอกจากเรื่องความสวยงามแล้ว ปัจจัยหลักในการพิจารณาเลือกใช้งาน ได้แก่ ความต้านทานการกัดกร่อน จากสภาวะอากาศ อายุการใช้งานและราคา การออกแบบวัสดุประเภทนี้ต้องให้ความสำคัญกับความเป็นระบบ ทั้งระบบการติดตั้ง การป้องกันน้ำ ความชื้นการรั่วซึมของอากาศ ผลิตภัณฑ์โลหะทางเลือกสำหรับงาน Metal Cladding เช่น เหล็กชุบสังกะสีผสมอะลูมิเนียม, เหล็กสเตนเลส, ทองแดง, ไททาเนียม, ไททาเนียมสังกะสี เป็นต้น
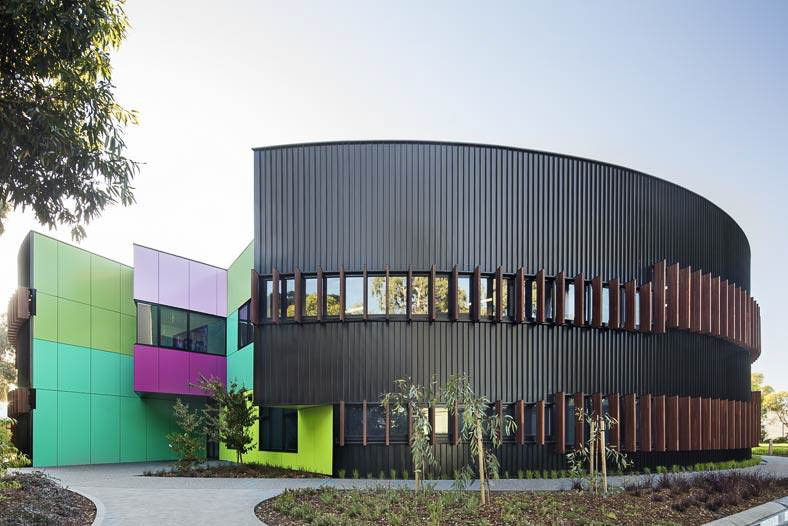

Photo: Dow
เหล็กสนิม หรือ Weathering Steel หรือ Weathered Steel เป็นโลหะผสมในกลุ่มของเหล็กที่มักใช้ในการก่อสร้างกลางแจ้ง ได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อลดความจำเป็นในการทาสี โดยหากปล่อยทิ้งไว้ภายนอกสัมผัสกับองค์ประกอบต่างๆ ก็จะเกิดสนิมขึ้นภายในเวลาเพียงไม่กี่เดือน เหล็กสนิมถูกนำมาใช้ในงานสถาปัตยกรรมด้วยความมีลักษณะเฉพาะด้านความสวยงามเป็นธรรมชาติ ในปี ค.ศ. 1930 U.S. Steel ได้ออกแบบพัฒนาผลิตภัณฑ์เพื่อสร้างทางรถไฟใช้ชื่อว่า Corten Steel และ COR-TEN ก็เป็นเครื่องหมายการค้าจดทะเบียนในเวลาต่อมา Weathering Steel มีความต้านทานการกัดกร่อนและต้านทานแรงดึงองค์ประกอบทางเคมีของเหล็กประเภทนี้ ทำให้สามารถต้านทานการกัดกร่อน ในชั้นบรรยากาศที่เพิ่มขึ้นเมื่อเทียบกับเหล็กอื่นๆ เนื่องจากเหล็กสร้างชั้นป้องกันบนพื้นผิวภายใต้อิทธิพลของสภาพอากาศ ชั้นปกป้องพื้นผิวจะพัฒนาและงอกใหม่อย่างต่อเนื่องเมื่ออยู่ภายใต้อิทธิพลของสภาพอากาศ อาจกล่าวว่าเหล็กสามารถเกิดสนิมเพื่อสร้างชั้นเคลือบป้องกันซึ่งมีความเสถียรได้
การนำเหล็กสนิมไปใช้งานต้องพิจารณาในเรื่องเทคนิคการเชื่อมต่อวัสดุ วัสดุเชื่อมที่ใช้ต้องมีอัตราการกัดกร่อนเช่นเดียวกับเหล็กสนิม ต้องมีการระบายไม่ให้มีการขังน้ำเกิดขึ้น การกัดกร่อนจากสภาวะอากาศในแต่ละพื้นที่ก็จะแตกต่างกันไป ในพื้นที่ที่มีมลพิษในอากาศสูงจะมีผลต่อความเสถียรของชั้นปกป้อง อาจทำให้ไม่สามารถหยุดยั้งการกัดกร่อนได้ การทำความสะอาดคราบสนิมที่จะไหลออกมายังต้องเป็นเรื่องคำานึงถึงด้วย การใช้งานผนังโลหะโปร่งระบายอากาศในลักษณะ Second Skin ปรากฏในงานสถาปัตยกรรมสมัยใหม่ออกแบบโดยสถาปนิกที่มีชื่อเสียง มีการนำโลหะรูปแบบต่างๆ มาประยุกต์ใช้งาน ผนังโลหะโปร่งในงานผนังภายนอกอาคารช่วยให้แสงสว่างธรรมชาติและอากาศผ่าน สร้างการเชื่อมโยงด้วยมองเห็นออกไปสู่ภายนอก แผ่นโลหะเจาะรู (Perforated Metal) นำเอาแผ่นโลหะบางต่างๆ เช่น แผ่นเหล็กกัลวาไนซ์ แผ่นเหล็กสเตนเลส แผ่นอะลูมิเนียม เป็นต้น มาเจาะรูตามการออก-แบบ การเจาะรูช่วยลดน้ำหนักของแผ่นผนังได้ในขณะที่ไม่ได้ลดความแข็งแรงลงมากนัก สร้างความน่าสนใจ สามารถออกแบบลวดลายที่มีความซับซ้อนต่างๆได้
ตะแกรงโลหะฉีก (Expanded Metal) เป็นการนำแผ่นโลหะมาทำการเจาะและฉีกให้เป็นช่องรูปร่างต่างๆ โดยมีมุมที่ยังคงยึดติดกันและต่อกันอย่างเป็นระเบียบ เป็นการเพิ่มความแข็งแรงของโครงสร้างโลหะและลดน้ำหนักของแผ่นโลหะในเวลาเดียวกัน ทำให้มีความแข็งแรง รับน้ำหนักบนแผ่นได้ไม่บิดงอหรือเสียรูป น้ำหนักเบา การใช้ในงานผนังอาคารลักษณะคล้ายกันกับแผ่นโลหะเจาะรู การใช้โลหะที่มีลักษณะเป็นเส้นมาถักทอให้เกิดเป็นตาข่ายหรือผืนผ้าโลหะ (Metal Fabric) มีลักษณะเฉพาะตัว ให้ความสวยงาม ทันสมัย ยืดหยุ่น เป็นตัวป้องกันความร้อนและแสงสว่างจากดวงอาทิตย์ ขณะเดียวกันก็สร้างความโปร่งเบา ปรับสภาพอากาศ สร้างพื้นที่ว่างที่น่าสนใจ โลหะหลักที่นำมาใช้ในงานผนังภายนอกอาคารเป็นเหล็กสเตนเลสคุณภาพสูง แต่โลหะอื่นก็สามารถนำามาใช้งานได้ เช่น ทองแดง อะลูมิเนียม เป็นต้น
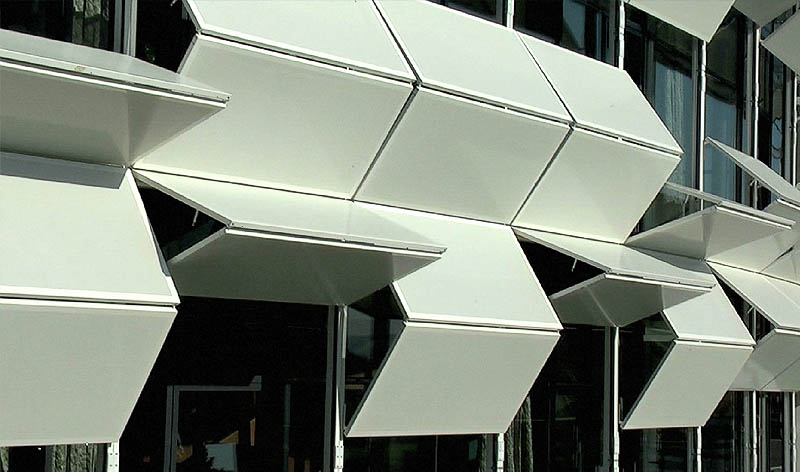
Photo: Media-TIC / Enric Ruiz Geli
Soft Material
วัสดุผ้าใบที่พัฒนาคุณภาพเพื่อการใช้งานภายนอกอาคาร ทนทานต่อสภาวะอากาศซึ่งมีความรุนแรง ถูกนำมาใช้เป็นผ้าใบขึงตึงในงานสถาปัตยกรรมด้วยลักษณะเฉพาะในความที่มีน้ำหนักเบา สร้างรูปทรงอิสระ และมีการส่องผ่านของแสงสว่างธรรมชาติ ช่วยป้องกันความร้อน ควบคุมปริมาณแสงสว่างและการมองเห็น สามารถทำการสื่อสารด้วยภาพบนพื้นผิว ช่วยปรับปรุงความน่าสบายทางด้าน Acoustic ทั้งภายในและภายนอกอาคาร นอกจากวัสดุผ้าใบเส้นใยสังเคราะห์ที่มีความบางเบา ยังมีความพยายามใช้วัสดุพื้นผิวที่อ่อนนุ่มพิเศษ เช่น แผ่นยาง พรมที่ใช้ในงานสถาปัตยกรรมเป็นต้น มาประยุกต์ใช้กับผิวอาคาร Gasser Fassadentechnik แห่ง St.Gallen ประเทศสวิสเซอร์แลนด์ นำเสนอวัสดุดังกล่าวเป็นวัสดุสำหรับอาคารที่ยั่งยืน
ยาง EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer Rubber) เป็นวัสดุอเนกประสงค์มีความยืดหยุ่นสูง ทนทานต่อสภาพอากาศ มีความทนทานต่อรังสี UV และมีความปลอดภัยจากเพลิงไหม้ในระดับ B1 หลังจากผ่านขั้นตอน การใช้งานแล้วสามารถหั่นเป็นชิ้นเล็กชิ้นน้อยเพื่อนำไปรีไซเคิลต่อไปได้ Tisca Tiara นำเสนอผลิตภัณฑ์วัสดุสนามหญ้าเทียม สำหรับสนามกีฬากลางแจ้งซึ่งมีความทนทาน เพื่อใช้กับผิวแนวตั้งภายนอกอาคาร หญ้าเทียมความหนา 32 มม. ทนทานต่อสภาพอากาศ ทนรังสี UV การประยุกต์ใช้งานแบบผิดวัตถุประสงค์พบว่าสร้างความน่าสนใจมากกว่าการเป็นพื้นสนามกีฬา
Kinetic Façade
การพัฒนาออกแบบงานสถาปัตยกรรมที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเคลื่อนที่ของวัตถุ แรงและพลังงานที่เกี่ยวข้องอย่างต่อเนื่องตอบสนองต่อสิ่งแวดล้อมกับเทคโนโลยีก้าวหน้าสร้างความน่าสนใจในหลายปีที่ผ่านมา Al Bahr Towers ของบริษัทสถาปนิก Aedas ในอาบูดาบี ออกแบบใหม่มีแผงคล้ายร่มของด้านหน้าอาคารควบคุมด้วยระบบคอมพิวเตอร์เปิดและปิดตอบสนองต่อการเคลื่อนไหวของดวงอาทิตย์ ปกป้องผู้ใช้อาคารจากความร้อนและแสงสะท้อน ลดความจำเป็นในการใช้เครื่องปรับอากาศ และทำให้อาคารมีความยั่งยืนมากขึ้น แผงเหล่านี้ยังได้รับแรงบันดาลใจทางศาสนาด้วยความเคารพในมรดกทางวัฒนธรรมด้วยพื้นผิวอาคารที่เคลื่อนไหวไม่หยุดนิ่ง ใช้ในการจัดการด้านแสงสว่าง อากาศพลังงาน และแม้แต่การสื่อสารด้านข้อมูลต่างๆ สามารถลดการรับแสงอาทิตย์ ปล่อยให้อากาศบริสุทธิ์ผ่านเข้าปรับสภาพแวดล้อมภายในอาคารอาจมีการตั้งโปรแกรมให้ตอบสนองต่อปัจจัยทางด้านสภาพแวดล้อม เวลาระดับ ลักษณะการเข้าใช้อาคาร และอื่นๆ เพื่อปรับปรุงประสิทธิภาพและประสิทธิผล
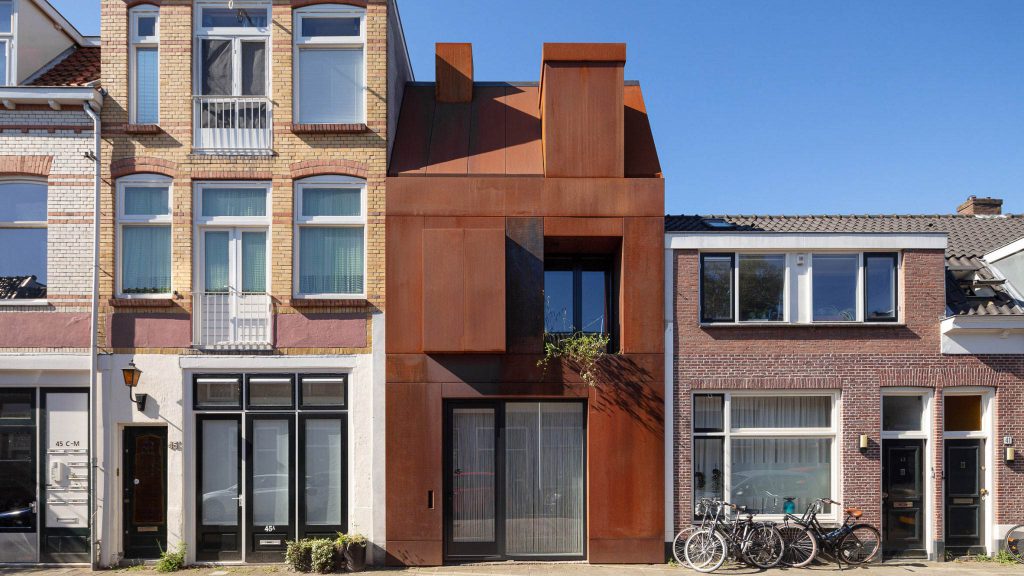

Photo: Dezeen
Advanced Building Skin
ความก้าวหน้าด้านเคมีและวัสดุศาสตร์ทำให้เกิดการพัฒนาต่อเนื่อง การประยุกต์ใช้เซลล์พลังงานแสงอาทิตย์กับงานผิวผนังอาคารได้พัฒนาใช้งานมาเป็นเวลานานแล้ว โลหะที่ปรับเปลี่ยนรูปทรงเมื่ออุณหภูมิเปลี่ยนแปลงได้มีการศึกษาทดลองเพื่อมาใช้ในงานอาคาร ผิวผนังซึ่งปกปิดด้วย Titanium Dioxide ช่วยฟอกอากาศโดยรอบให้บริสุทธิ์ ขจัดมลพิษอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพโดยการปล่อยอนุมูลอิสระที่ลักษณะเป็นรูพรุน กระเบื้อง Prosolve370e พัฒนาโดยบริษัทสัญชาติเยอรมันชื่อ Elegant Embellishments ทำให้เกิดรูปแบบที่ออกแบบปรับแต่งได้ เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพ การทำงานโดยการเร่งปฏิกิริยาด้วยแสง (Photocatalyst) สามารถล้างและกำจัดสารพิษที่เป็นอันตรายได้ด้วยพลังของแสงที่เข้ามาใกล้พื้นผิวเคลือบด้วย สารที่สามารถเร่งปฏิกิริยาด้วยแสง สิ่งที่สามารถกำจัดได้ เช่น กลิ่นเหม็นจากของสกปรก แบคทีเรีย เชื้อโรคต่างๆ เชื้อรา ไวรัส และสารเคมีที่ทำให้มีอาการป่วยได้
กลุ่มนักออกแบบ Splitterwerk Architects และ Arup ได้ทำการทดสอบกับผนังอาคารในประเทศเยอรมนีขนาด 200 ตารางเมตร โดยการใช้ตะไคร้น้ำขนาดเล็กมากมายหลายล้านต้นให้ได้รับสารอาหารและก๊าซออกซิเจนเพื่อไปกระตุ้นการผลิตสารชีวมวล เซลล์เล็กๆ ที่ได้รับแสงอาทิตย์โดยตรงจะเติบโตอย่างรวดเร็วส่งผลให้น้ำมีอุณหภูมิสูงขึ้น ระบบจะกักเก็บความร้อนนั้นเพื่อไว้ใช้ในอาคารต่อไป กลายเป็นแหล่งพลังงานที่ยั่งยืนเปลี่ยนสภาพแวดล้อมในเมืองได้ อาคาร Habitat 2020 สร้างขึ้นในประเทศจีนเปลี่ยนแปลงการรับรู้ของเราเกี่ยวกับพื้นผิวโครงสร้างอย่างมาก ภายนอกได้รับการออกแบบให้เป็นพื้นผิวที่มีชีวิต ซึ่งแตกต่างจากวัสดุก่อสร้างที่นิ่งเฉยทั่วไป ผิวหนังลักษณะเยื่อหุ้มทำหน้าที่เป็นตัวเชื่อมระหว่างภายนอกและภายในของที่อยู่อาศัย ในมุมหนึ่งผิวห่อหุ้มอาจพิจารณาเป็นผิวใบที่มีปากใบหลายช่อง ช่องเปิดของเซลล์เกี่ยวข้องกับการแลกเปลี่ยนก๊าซและการคายน้ำในพืช
พื้นผิวที่ช่วยให้แสงสว่าง อากาศ และน้ำผ่านเข้าไปสู่ที่พักอาศัย มีการจัดการตัวเองโดยอัตโนมัติตามแสงอาทิตย์ที่สาดส่องเข้ามา จึงไม่จำเป็นต้องมีไฟฟ้าสำหรับแสงสว่างในตอนกลางวัน อากาศและลมจะถูกส่งเข้าสู่อาคารโดยมีการกรองเพื่อให้เป็นเครื่องปรับอากาศตามธรรมชาติที่ให้อากาศบริสุทธิ์ พื้นผิวมีการตอบสนองสามารถกักเก็บน้ำฝน โดยน้ำนั้นจะถูกทำให้บริสุทธิ์ กรอง น้ำไปใช้และรีไซเคิล พื้นผิวยังสามารถดูดซับความชื้นจากอากาศ ของเสียที่เกิดขึ้นจะถูกแปลงเป็นพลังงานก๊าซชีวภาพ ซึ่งสามารถนำไปใช้ประโยชน์ต่างๆ ในแหล่งที่อยู่อาศัยได้ด้วย

Photo: Detail-online
ในวันนี้ยังคงมีวัสดุผิวผนังมากมายให้สถาปนิกได้พิจารณาเลือกใช้ในงานออกแบบสถาปัตยกรรม ตัวอย่างวัสดุหนึ่งที่มีใช้งานแพร่หลายแต่ยังไม่ได้กล่าวถึง ได้แก่ กระจก ซึ่งอาคารสมัยใหม่ออกแบบระบบผนัง Curtain Wall ใช้กระจกประสิทธิภาพสูง ให้แสงสว่างผ่านเข้าสู่ภายในอาคารในขณะที่ช่วยป้องกันความร้อนที่จะผ่านเข้าสู่ภายในอาคาร ระบบ Curtain Wall มีการออกแบบให้ป้องกันการรั่วซึมของน้ำและอากาศได้เป็นอย่างดี ต้องย้ำว่าการออกแบบรายละเอียดเป็นเรื่องสำคัญมาก สถาปนิกต้องรู้จักในวัสดุที่นำมาใช้งาน เพื่อประสิทธิภาพ ประสิทธิผล ความยั่งยืน และหลีกเลี่ยงปัญหาที่อาจจะตามมาในอนาคต ไม่ต้องไปเป็นภาระให้กับทางโครงการและผู้เข้ามาใช้อาคาร
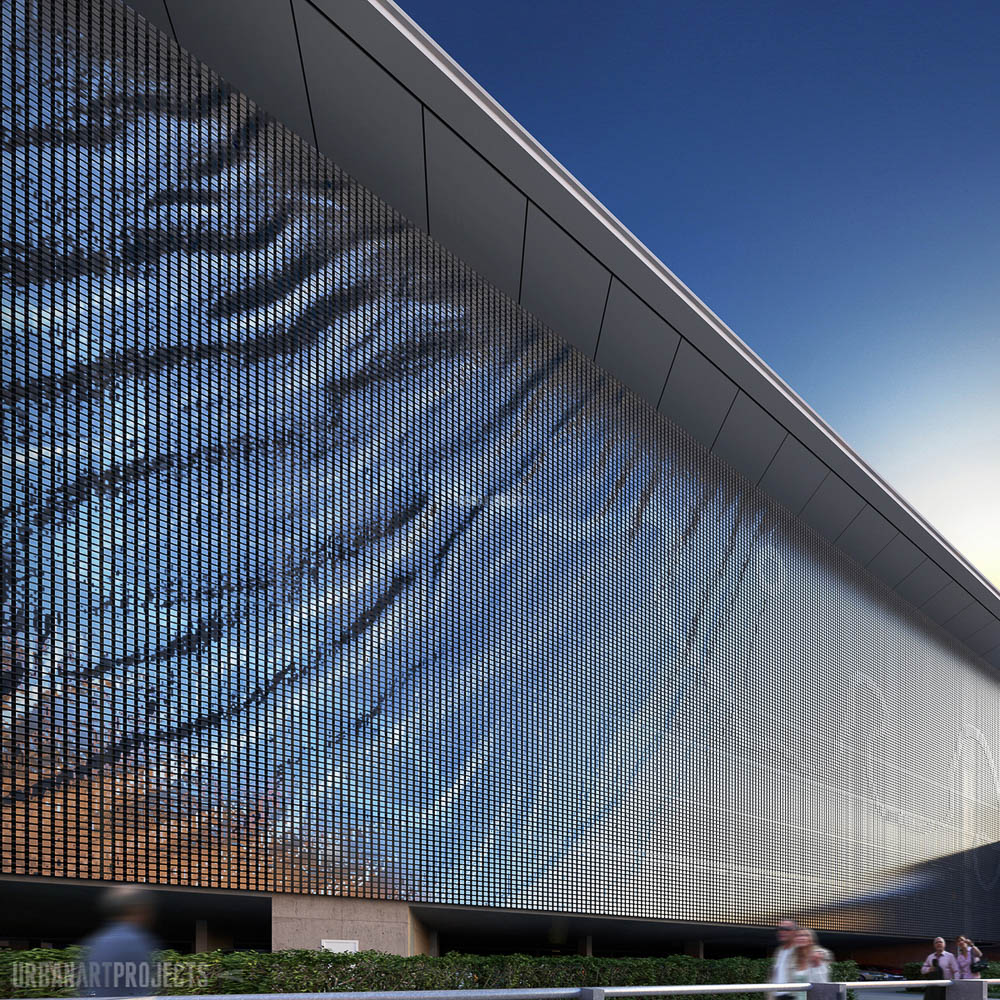

Photo: Galleria Centercity / UNStudio
External Cladding
Ludwig Hatschek created fiber cement in the late 19th century. Boarding made from this material, which is composed of cement, cellulose, and various minerals later became widely used. This material is unique in its rawness. It was produced and introduced for different uses and is a product whose qualities ensure suitability in exterior applications. The material can be drilled with waterjet or CNC machined allowing for different patterns of embossing and other finishes. Design detailing is very important here particularly for exterior walling, panel joints, installation systems and supporting structure all affect efficiencies in relation to insulation, ventilation, water tightness and energy management.
Aluminium is another modern cladding material used in architectural work in sheet or panel guise due to its attributes. The material is generally aesthetically pleasing, lightweight and allows for flexibility and ease of installation. Both its natural and applied coatings offer durability and a long-life span with generally minimum maintenance. This type of material is available in both solid and composite format. Solid aluminium sheets and panels are safe and environmental friendly. Two types of ready-made coatings for this type of panel include high quality fluorocarbon color coating and an anodized coating. Composite aluminium sandwich panels are composed of two thin aluminium sheets with an inert fire-resistant core in the middle. The outer layers are generally coated by weather-resistant fluorocarbon while the fire resistant / FR core, as well as the honeycomb aluminium core are used for durability.
Mechanical fixing system is the standard and popular method of installation even though high-quality adhesives are available and developed as an alternative. As with any cladding system, particular care is needed in the design of jointing and sealants as well as attention to maintenance, reparation and cleaning methods. Metal cladding is strong, durable, and flexible, various types of metal have different attributes, aesthetic appeal and cost. Some of these receive factory pre-coatings while some do not. Other types of metal see change in physical attributes over time, giving them life-like quality and offering alternative applications in architectural design and use. Other factors for consideration when choosing which materials to use is its resistance to adverse weather conditions, durability / longevity, installation methodology and cost. Cladding materials that fall into this category include coated steel, coated aluminium, zinc anneal, stainless steel, copper, brass, titanium, titanium-zinc, and others.
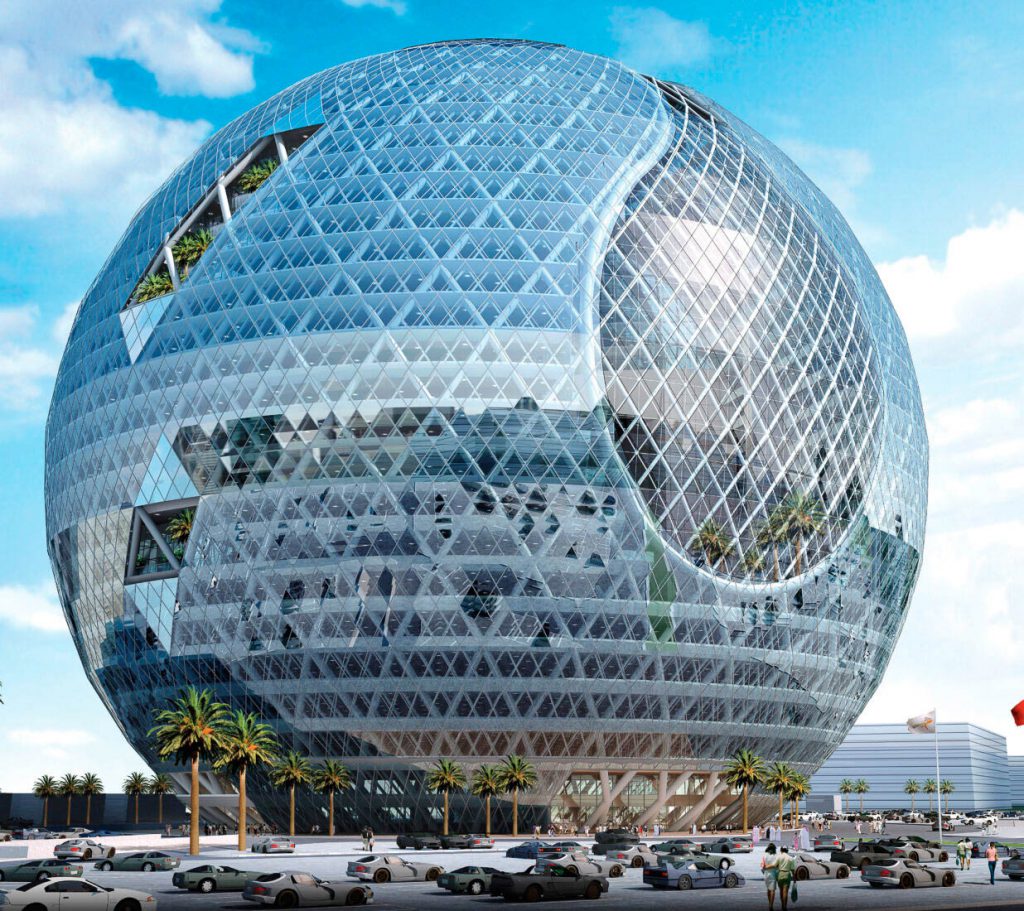

Photo: Architectsjournal
Weathering Steel or Weathered Steel is an alloy of steel often used in outdoor construction. It is originally designed to reduce the need for paint. If left outdoor in contact with weather and various elements, it will rust in just a few months. Weathering steel thus is widely used in architecture for its natural beauty features. In 1930, U.S. Steel developed a product for railway construction under the name of Corten Steel, which later was signed under the patent name of COR-TEN. It is a weathering steel more resistant to atmospheric corrosion due to its chemical compounds that creates a protective surface layer. It is a composite steel alloy developed to eliminate the need for the application of finishes forming a stable rust-like appearance showcasing its unique natural beauty after several months to years of weather exposure. As such, the material is generally used in outdoor applications.
There are several factors to consider when utilizing this type of material. The first is welding, as material used in welding needs to have the same corrosion rate as that of the weathering steel. Also, corrosion occurs differently in different weather conditions and high levels of air pollution also impacts on the stability of the protection layer, which in turn affects its ability to resist corrosion. Applications require adequate ventilation to prevent water collecting and any rust run-off needs cleaning. In the past few decades the use of airy metal walls including wire mesh and perforated steel sheet in the form of Second Skin appears in modern architecture designed by renowned architects. This type of cladding uses thin sheets made from different types of metal such as aluminium, galvanized and stainless steel. Sheets can be perforated in a variety of interesting patterns in this type of application. The holes lead to a reduction in weight while retaining material strength and integrity. Perforations also allow for natural light, ventilation and visual connectivity to adjoining environments as well as provide freedom for architects to design patterns of various complexity.
Expanded metal involves drilling and expanding metal sheets to create perforations in different three dimensional shapes which simultaneously increases the metal structure’s strength and capacity while reducing. The sheets can carry weight without bending or deforming. Uses in cladding and walling are quite similar to that of perforated metals. Metal fabrics are metals which are woven together into nets or fabrics. They are unique, beautiful, modern, and flexible. This type of cladding offers protection against heat gain and sunlight while providing a feeling of transparency. They also help condition the air and create interesting spaces. This system generally uses high quality stainless steel, although other materials such as zinc and aluminium are available.

Photo: Professionals.lysaght
Soft Material
High quality, weather-resistant canvases and like materials are developed for exterior use and can serve as tension membranes for architectural applications. Their unique qualities include lightness, an ability to create free forms and options in light transparency which can be manipulated to the level of heat, light and visibility required. Their surface can also double as image projectors in facilitating communications. The materials can also improve building acoustic comfort internally and externally. Apart from lightweight synthetic canvases, there are applications of materials with especially soft surfaces, such as rubber sheets or carpet for architectural use in walling. Gasser Fassadentechnik from St. Gallen, Switzerland offers them as alternatives for sustainable buildings.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer or EPDM membranes is a multipurpose rubber like material with high flexibility, weather, UV resistance, B1-level fire safety and recyclable properties. Tisca Tiara offers products made from similar materials to and as durable as artificial grass for outdoor stadiums for cladding applications. UV and weather-resistance of the artificial material has shown that it can be utilized in many building types other than sport stadiums.
Kinetic Façades
In recent years, there have been interesting and on-going development in architecture relating to the movement of objects, forces and energy which responds to the environment through advancing technology. Al Bahr Towers in Abu Dhabi, designed by Aedas, incorporates such technology through computer controlled, umbrella-like panels. Panels open and close in relation to the suns positioning and serve to protect the user and building from heat and light reflection reducing reliance on mechanical air conditioning systems for a more sustainable building outcome. Panel design is often inspired by religion, displaying the designer’s reference to cultural heritage.
Moving cladding systems are also used to manage light, ventilation, energy and even communication. They can mitigate the building’s exposure to sunlight and let fresh air flow through and condition the interior environment. Responses to different factors in the environment, time, levels and manners of use, and others can be programmed to improve effectiveness and efficiency.
Aluminium Cladding
Photo: AlucobondPerforated Metal
Photo: Alucobond
Advanced Building Skin
Advances in modern chemistry and material science has led to constant and positive progress such as the development and application of photovoltaics (PV) on wall and roof cladding. There are also on-going experiments utilizing metals whose shapes shift in relation to the temperature on buildings and claddings enclosed in titanium dioxide help clean the surrounding air eliminating toxins effectively by releasing hole-shaped free radicals. Prosolve 370e tiles, were developed by the Germany firm, Elegant Embellishments and can be manipulated into different shapes. Their surfaces are coated in special chemicals that can magnify the light by photocatalysis which is a process where light is magnified when in contact with the chemicals. This process eliminates harmful toxins and micro-organisms that lead to illnesses as well as the undesirable odors resulting from those substances and organisms.
Splitterwerk Architects and Arup experimented on a 200 square meter wall surface in Germany allowing millions of microalgae to receive nutrients and oxygen to stimulate biomass production. As an example, small cells receiving sunlight directly grow quickly which heightens water temperature providing heat which can be stored by for future use in buildings. This alternate energy system will become a sustainable source of energy improving the environment in cities. The Habitat 2020 building in China drastically changes our perception of surface structures. The materials used in the exterior cladding, unlike static architecture is designed to be organic. The membrane-like cladding serves to connect the interior and exterior of the building, the cladding seen as a ‘leaf’ type surface with multiple stomata or open cell membranes pertaining to the exchange of gases and transpiration of water.
The cladding works by itself in contact with sunlight, air and water flow into the building. This in turn diminishes the reliance on artificial lighting during the daytime. Pressured air flows into the building through filters that naturally condition and purify and is stored for use and recycling. The design allows absorption of moisture in the air and any resultant waste is converted into biogas energy that serves different building functions.
These days there are many different cladding materials and systems that the architect can select for use in their design, however the most common and widely used material not yet discussed is glass. Modern architecture uses curtain walling and high-quality glass that allows light penetration but reflects thermal heat and UV. These materials and systems are also air and water penetration resistant designed for efficiency.
Again, proper detail design is of high importance in terms of overall material and system functionality and efficiency. To that end, architects need to possess the relevant knowledge and experience for the design to be effective, efficient, and sustainable avoiding potential issues that would otherwise consequently arise.



